Blockchain is no longer just the technology behind Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies.
Beyond digital coins, blockchain is disrupting core industries by enhancing transparency, security, efficiency, and automation.
From food to energy to real estate, its real-world impact is profound—and only just beginning.
Below, explore five key industries being reshaped by blockchain, Blockchain disrupting industries with case studies, benefits, challenges, and future outlooks.
5 Real Industries Blockchain Is Disrupting
Blockchain is revolutionizing industries far beyond cryptocurrency. From supply chain and healthcare to real estate, digital identity, and energy, it’s enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency.
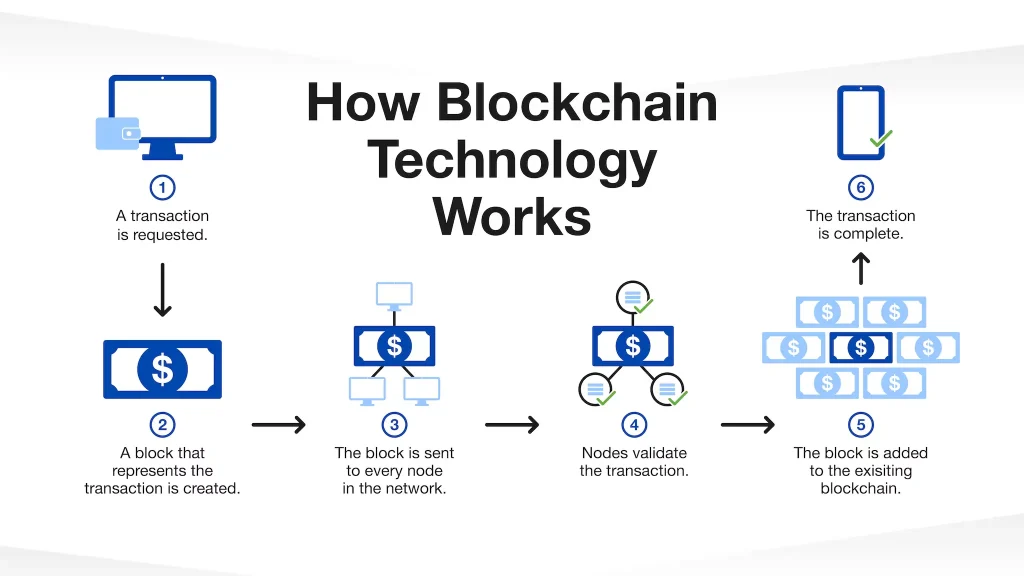
These five sectors are embracing blockchain to automate operations, Real-world blockchain use cases, reduce fraud, and empower users—marking just the beginning of a global digital transformation.
1. Supply Chain & Logistics
Current Challenges
- Opaque supply chains with limited traceability
- Counterfeit or contaminated products
- Manual documentation, delays, and high costs
How Blockchain Helps
A permissioned blockchain serves as a shared, immutable ledger among suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers. Immutable data combined Blockchain industry disruption, with IoT sensors, QR codes, or RFID tags enables real-time tracking and enhanced trust.
Real-World Examples
- IBM Food Trust: Partners like Nestlé and Walmart use it to trace produce within seconds.
- OpenSC: WWF + BCG platform lets consumers verify sustainable sourcing via QR codes.
- Mercedes-Benz: Uses blockchain to monitor CO₂ emissions and uphold ethical standards in its battery-cell supply chains.
Benefits
- Fast recall and contamination response
- Provenance verification and counterfeit prevention
- Lower admin time, back-office costs, and improved IoT integration.
Challenges
- Scalability issues with legacy ERP integration
- Need for interoperability and standardized approaches
Future Outlook
Blockchain and IoT convergence promises predictive risk management and fully transparent, traceable global supply ecosystems
2. Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
Industry Pain Points
- Fragmented patient data and privacy concerns
- Drug counterfeiting along pharmaceutical supply chains
- Research integrity and trial transparency
Blockchain Solutions
Decentralized ledger for Electronic Health Records (EHRs), tamper-proof clinical trials, and fully traceable drug journeys

Real-World Examples
- Guardtime (Estonia): Secures over 1 million national health records
- Medicalchain: Puts patients in control of data
- MediLedger: Prevents counterfeit drugs through supply chain tracking
Benefits
- Normalizes secure, interoperable EHR sharing
- Ensures clinical trial data integrity
- Cuts fraud and ensures drug authenticity
Challenges
- Stringent healthcare regulatory requirements
- Patient consent and scalable implementation
Future Outlook
Expect blockchain-enabled health records exchanged seamlessly across borders, smart contract-based insurance payouts, and regulation-compliant ecosystem platforms.
3. Real Estate & Property Management
Market Issues
- Complex title transfers and manual paperwork
- Fraud, time-consuming intermediaries, and high costs
- Difficult asset shareability and liquidity
Blockchain Impact
- Land registries via immutable ledgers
- Tokenized property sale and fractional ownership
- Smart contract–based rentals and automated transactions
Real-World Case Studies
- Propy & RealT: Allow end-to-end blockchain real estate transactions and fractional rentals
- Sweden & UAE pilot programs: Use blockchain for national land title recording
Benefits
- Reduced fraud via secure title traceability
- Lower costs and faster transactions
- Liquidity through property tokenization
Challenges
- Legal system coherence and cross-border regulatory alignment
- Market acceptance of digital registries
Future Outlook
Move toward interoperable global land registries and universal smart contract–facilitated rental and leasing platforms.
4. Digital Identity & Governance
Identity Weaknesses
- Centralized databases vulnerable to breaches
- Lack of user control and data privacy
- Voter fraud and lack of trust in elections
Blockchain Approach
- Self‑Sovereign Identity (SSI) where users control credentials via decentralized IDs
- Blockchain voting systems ensuring transparency and tamper-proof votes
Real Deployments
- Microsoft ION and ID2020: Global DID networks
- Voatz & Horizon State: Facilitate secure mobile voting
- China RealDID: National blockchain‑based ID replicating real‑name verification
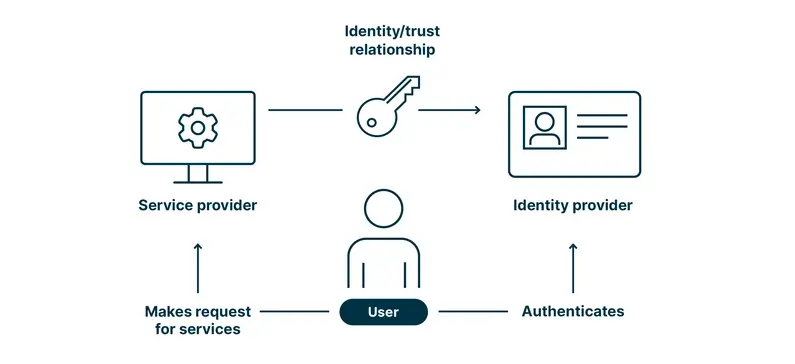
Benefits
- Enhanced user privacy and data control
- Streamlined KYC processes
- Verifiable, transparent elections and civic tech frameworks
Challenges
- GDPR compliance and the “right to be forgotten”
- Adoption and demographic trust
Future Outlook
Integration of DID in telecom, banking, and government, plus secure mobile voting capabilities.
5. Energy & Utilities
Traditional Sector Flaws
- Centralized energy grids lacking flexibility
- Poor management of renewable sources
- Limited consumer control over energy trading
Blockchain Innovations
- Peer-to-peer energy trading networks
- Smart contracts handling dynamic energy pricing and settlements
Notable Initiatives
- WePower (Estonia): Blockchain tokens for renewable energy trade
- Brooklyn microgrid: Local solar energy peer‑trading via smart contracts
Benefits
- Efficient, localized energy distribution
- Incentivizes green energy usage
- Consumers earn from excess power generation
Challenges
- Scalability and on-chain transaction volume
- Governing regulation and interoperability
Future Outlook
Emerging Internet of Energy Networks like IOEN using blockchain for scalable microgrid management
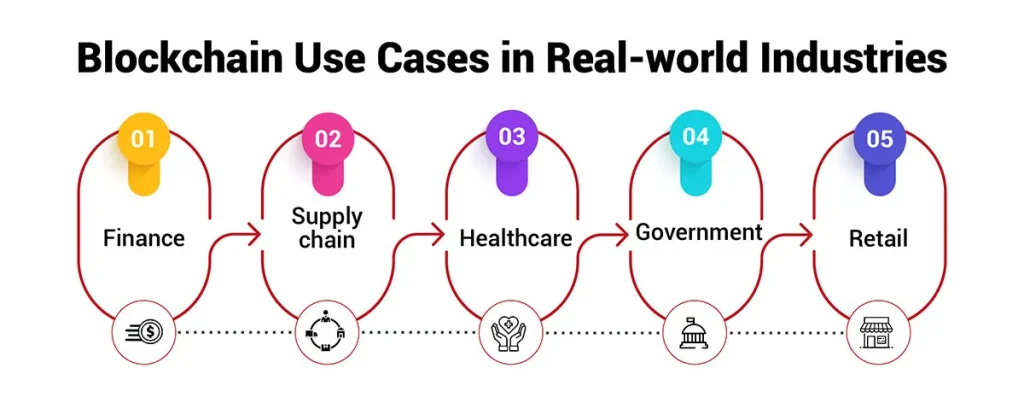
Why It’s Just Beginning
1. Regulatory Tailwinds
Governments are exploring blockchain for land, voting, identity, and financial systems—indicative of deeper future adoption.
2. Tokenization of Assets
Real-world assets like real estate, carbon credits, private equity, and bonds are being tokenized via networks like Redbelly
3. Converging Tech
Blockchain + AI + IoT = self-executing, trusted ecosystems (e.g., smart supply chains, smart homes).
4. Corporate Momentum
Global enterprises across industries report that 81% are exploring blockchain solutions .
Comparison Table of Disrupted Industries
| Industry | Blockchain Role | Key Benefits | Major Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain | Immutability, tracking, IoT integration | Traceability, fraud prevention, cost-cutting | Integration, scalability |
| Healthcare | EHR, trial records, drug tracking | Security, patient control, authenticity | Regulation, privacy, complexity |
| Real Estate | Title registry, tokenization, smart deals | Fraud reduction, liquidity, automation | Legal changes, adoption resistance |
| Identity & Voting | Self-sovereign identity, transparent voting | Privacy, control, fraud-proof elections | GDPR, technical trust |
| Energy & Utilities | P2P energy trading, microgrid smart systems | Efficiency, green incentives, autonomy | Volume, regulation, standardization |
Blockchain’s potential extends far beyond finance and crypto. In supply chains, healthcare, real estate, identity, and energy, it’s rewriting established systems—and this is only the beginning.
With continued improvements in scalability, regulation, and cross-sector adoption, blockchain is moving from experimentation to essential infrastructure.
Its impact will grow every year, creating smarter, fairer, and more efficient systems worldwide.

