Picture this: You decide to buy your first NFT, feeling like a digital art connoisseur ready to join the elite club of blockchain enthusiasts. You’ve got $100 worth of Ethereum in your wallet, and you’ve found the perfect $50 digital masterpiece.
You hit “buy now” and suddenly… WHAM! The network wants $75 in gas fees just to process your transaction.
Welcome to the wonderful world of blockchain gas fees — where sending $10 can cost you $20, and where the phrase “the transaction failed but we kept your fee anyway” has made grown crypto investors weep into their keyboards12.
If you’ve ever stared at your screen wondering why moving digital money costs more than your morning coffee, you’re not alone.
Gas fees are the cryptocurrency world’s equivalent of that friend who always “forgets” their wallet when the dinner bill arrives — except this friend is a mathematical algorithm, and they NEVER forget to charge you.
Gas Fees Explained: The Digital Toll Booth That Never Sleeps
What Exactly ARE Gas Fees?
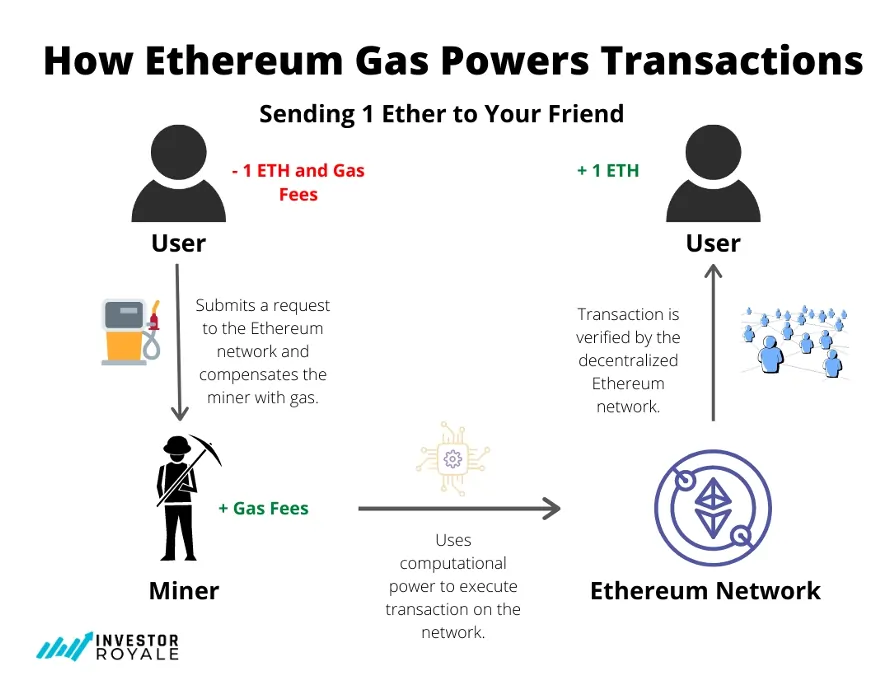
Think of blockchain networks like busy highways, and gas fees as the tolls you pay to use those highways. But here’s where it gets interesting — gas fees aren’t just simple transaction charges. They’re actually the fuel that powers the entire blockchain ecosystem.

In the blockchain world, “gas” represents the computational effort required to execute operations. Every time you:
- Send cryptocurrency to someone
- Buy or sell an NFT
- Interact with a smart contract
- Stake your tokens
- Even when transactions FAIL
…you’re essentially hiring a network of computers to do mathematical work for you, and just like any workforce, they want to get paid.
The Ethereum Gas Station: Where Prices Change by the Minute
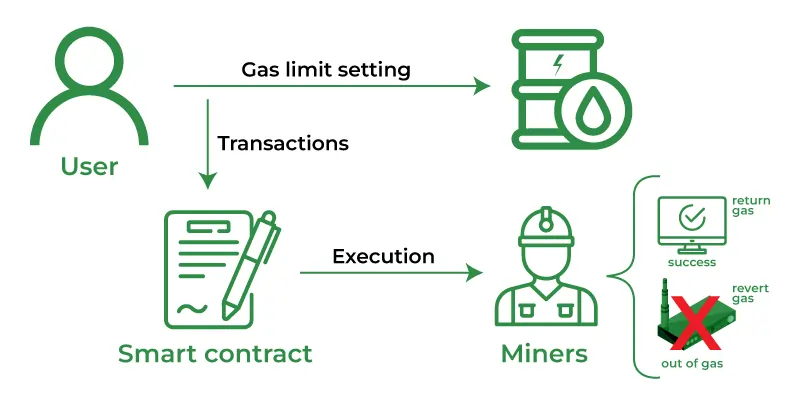
Ethereum uses a gas system that’s more complex than your local tax code. Here’s how it breaks down:
| Gas Component | What It Does | Real-World Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Limit | Maximum gas you’re willing to use | Your car’s gas tank size |
| Gas Price | How much you pay per unit of gas | Price per gallon at the pump |
| Gas Used | Actual gas consumed by transaction | How much fuel you actually used |
| Total Fee | Gas Used × Gas Price | Your total bill at the gas station |
“Gas fees are the charges users pay to compensate for the computing energy required to process and validate transactions on the blockchain network.”
The Great Gas Fee Mystery: Why Are They So Damn Expensive?
Supply and Demand: The Oldest Story in Economics
The brutal truth about gas fees is that they follow the most basic economic principle known to humanity: when everyone wants something at the same time, prices go through the roof.
Imagine if there was only one pizza delivery guy in your entire city, and everyone decided to order pizza simultaneously during the Super Bowl.
That poor delivery guy would start auctioning off his services to the highest bidder. That’s essentially what happens on busy blockchain networks.
During network congestion:
- DeFi applications launch (everyone rushes to trade)
- Popular NFT drops happen (digital art frenzy begins)
- Major market movements occur (panic buying/selling ensues)
- Network capacity remains the same (the bottleneck tightens)
The Ethereum Traffic Jam: A Case Study in Digital Frustration
Ethereum, being the most popular smart contract platform, suffers from what developers politely call “scalability challenges” and what users more accurately describe as “highway robbery.”
Peak congestion periods that make users cry:
- NFT Mint Days: When popular projects launch, gas fees often hit $100-300 per transaction
- DeFi Yield Farming Frenzies: New protocols can push fees to $50-150
- Market Crash/Pump Days: Panic trading can make a simple swap cost $200+
- Airdrop Claims: Free tokens that cost $75 in gas to claim (the irony is painful)
“During peak congestion, I’ve seen people pay $400 in gas fees to claim a $200 airdrop. It’s like paying $50 for shipping on a $25 item, except worse because it’s math, not just poor business decisions.”
The Hall of Fame: Most Expensive Gas Fee Horror Stories
When Gas Fees Become More Expensive Than Your Transaction
Let me share some real-world scenarios that’ll make you laugh… or cry:
The $10,000 Pizza Order: Someone tried to buy a $20 digital collectible during a major NFT drop. The gas fee? $85. They tried again thinking it was a glitch.
Another $85. By the fifth attempt, they’d spent $425 in gas fees and still didn’t own the $20 NFT.
The Failed Transaction Massacre: During the Ethereum 2.0 staking rush, thousands of users paid $50-100 in gas fees for transactions that failed due to network congestion. The kicker? Failed transactions still consume gas fees.
The Accidental Millionaire Move: A user accidentally set their gas price 100x higher than needed, paying $9,500 to send $120 worth of Ethereum. The transaction went through in record time, but their wallet didn’t recover for months.
Breaking Down the Numbers: What You’re Really Paying For
The Anatomy of an Expensive Transaction
Let’s dissect a typical expensive Ethereum transaction to understand where your money goes:
| Transaction Type | Typical Gas Units | During Normal Times | During Congestion | Why It Varies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple ETH Transfer | 21,000 | $3-8 | $20-50 | Basic computational work |
| Token Swap (Uniswap) | 150,000 | $20-40 | $100-200 | Complex smart contract interactions |
| NFT Purchase | 200,000 | $25-50 | $150-300 | Multiple contract calls and verifications |
| DeFi Yield Farming | 300,000+ | $40-80 | $200-400 | Multiple protocol interactions |
The Miners’ Perspective: Why They Love High Fees
Here’s something that might make you feel slightly better about those expensive fees: the people processing your transactions (miners/validators) are actually working incredibly hard.
What miners do for your gas fees:
- Run expensive computer equipment 24/7
- Consume significant amounts of electricity
- Maintain network security and decentralization
- Process thousands of transactions simultaneously
- Risk their own stake/investment in the network
Think of it this way: you’re not just paying for a transaction — you’re paying for a small slice of one of the most secure, decentralized computing networks ever created.
Smart Strategies: How to Survive the Gas Fee Apocalypse
Timing Is Everything: The Art of Gas Fee Ninja Moves
Best Times to Transact (Lower Gas Fees):
- Weekends: Especially Saturday mornings (UTC time)
- Late Night/Early Morning: 2-6 AM UTC when Asia sleeps and America dreams
- Avoid Monday Mornings: When the business world wakes up hungry for DeFi
Worst Times (Wallet-Draining Periods):
- Major NFT Drops: Wednesday-Friday afternoons
- DeFi Protocol Launches: Usually coincide with US market hours
- Market Volatility: During major price movements in either direction
Tools That Can Save Your Sanity (And Your Money)
| Tool/Strategy | How It Helps | Potential Savings |
|---|---|---|
| ETH Gas Station | Real-time gas price tracking | 20-50% by timing |
| Gas Price Alerts | Notifications when fees drop | 30-60% by patience |
| Layer 2 Solutions | Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism | 90-95% fee reduction |
| Gas Token Strategies | CHI tokens, GST | 10-40% on large transactions |
| Batching Transactions | Multiple operations in one transaction | 50-70% on multiple actions |
Layer 2: The Underground Railroad of Crypto
Layer 2 solutions are like finding a secret tunnel under a traffic jam. While everyone else sits in Ethereum’s expensive traffic, you can zip through side routes at a fraction of the cost.
Popular Layer 2 Options:
- Polygon (MATIC): Fees often under $0.01
- Arbitrum: 90%+ fee reduction compared to Ethereum
- Optimism: Similar savings with growing ecosystem
- Loopring: Specialized for trading with minimal fees
“Layer 2 solutions have been a game-changer. What used to cost me $100 in gas fees on Ethereum mainnet now costs me $0.50 on Polygon. It’s like discovering that expensive restaurant has a food truck serving the same meals for 1% of the price.”
The Psychology of Gas Fee Pain: Why It Hurts So Much
The Emotional Roller Coaster
There’s something uniquely frustrating about gas fees that goes beyond just losing money. It’s the unpredictability combined with the feeling of being held hostage by mathematics.
The Five Stages of Gas Fee Grief:
- Denial: “This can’t be right, let me refresh the page”
- Anger: “This is highway robbery! I’m never using this network again!”
- Bargaining: “Maybe if I wait 10 minutes, the fee will drop to something reasonable”
- Depression: “I just paid $80 to move $50. I’m terrible with money”
- Acceptance: “Well, at least I’m supporting network security… right?”
The Sunk Cost Fallacy Trap
Gas fees create a unique psychological trap: once you’ve started a transaction flow, you feel pressured to complete it even when fees spike.
It’s like being halfway through an expensive toll road — turning back feels like giving up, even when it might be the smarter financial choice.
The Future: Light at the End of the Gas Fee Tunnel?
Ethereum 2.0 and The Great Gas Fee Hope
Ethereum 2.0 promises to be the superhero we’ve all been waiting for, swooping in to save us from gas fee villains. The transition from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake, combined with sharding, could potentially:
- Increase network capacity by 100x or more
- Reduce gas fees by 90-99%
- Make blockchain technology accessible to regular humans again
- Allow you to buy that $5 NFT without taking out a second mortgage
Alternative Networks: The Competition Heats Up
Other blockchain networks are laughing at Ethereum’s gas fee problem while building user bases:
- Solana: Fees typically under $0.01
- Binance Smart Chain: Usually $0.10-1.00 per transaction
- Avalanche: Fast and affordable alternative
- Cardano: Predictable, low-cost transactions
Living With Gas Fees Until We Don’t Have To
Gas fees are simultaneously the most frustrating and most important aspect of blockchain technology.
They’re expensive because the networks are popular, and they’re popular because the technology is revolutionary12.
The key survival strategies:
- Time your transactions during off-peak hours
- Use Layer 2 solutions whenever possible
- Batch multiple actions into single transactions
- Consider alternative networks for routine operations
- Accept that some fees are worth paying for network security and decentralization
The Silver Lining
Here’s the thing that keeps us all coming back despite the gas fee pain: we’re participating in the construction of the future financial system.
Every transaction, no matter how expensive, is a vote for a more decentralized, transparent, and globally accessible financial infrastructure.
Sure, paying $50 to send $100 feels ridiculous today. But remember when sending an email cost money and took hours?
Technology evolves, costs decrease, and what seems impossibly expensive today becomes tomorrow’s footnote in history books.
Gas fees are the growing pains of revolutionary technology. They’re expensive, frustrating, and sometimes seem designed to separate us from our hard-earned crypto. But they’re also the fuel powering the most significant financial innovation since the invention of banking itself.
So the next time you’re staring at a $100 gas fee for a $20 transaction, take a deep breath, maybe wait for a better time, and remember: you’re not just moving money — you’re helping build the future. Even if that future is currently under expensive construction.
The blockchain revolution will continue, gas fees will eventually become reasonable, and someday we’ll tell our grandchildren about the time when moving digital money cost more than the money itself. Until then, may your gas fees be low and your transaction times be fast!