Ever watched Netflix and wondered how each episode builds on the last—creating an uneditable story everyone sees the same way? That’s how blockchain works, but instead of shows, it stores trustworthy data. Welcome to a world where code replaces middlemen, and information flows securely across the globe.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records data across multiple computers. Each “block” contains information linked to the previous one, forming a chain.
It’s transparent, tamper-proof, and doesn’t require central control. Commonly used in cryptocurrency, it’s also transforming finance, supply chains, healthcare, and identity systems.
Why Everyone’s Talking About Blockchain
From finance and real estate to gaming and voting, blockchain is everywhere. How secure is blockchain technology? But what exactly is it?
Blockchain isn’t just about Bitcoin—it’s a framework for storing data in a way that’s transparent, decentralized, and permanent. And while it sounds technical, you’re about to get blockchain explained using something you already understand: Netflix.
Netflix Analogy: The Easiest Way to Understand Blockchain
Let’s say you’re watching Stranger Things on Netflix.
- Every episode = a block of data
- Episodes are watched in order = data is stored sequentially
- You can’t skip, alter, or delete episodes = data is immutable
- Everyone watches the same version = decentralized trust
Now, swap TV shows for digital transactions—money transfers, health records, voting data—and you’ve got a blockchain.
Blockchain Explained: The Real Definition
Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger—a database that lives across multiple devices (nodes), What is blockchain technology? How secure is blockchain technology? not on a central server.
Each block stores:
- Transaction/data
- Timestamp
- Unique ID (hash)
- Reference to the previous block
This creates a chain of records, What is blockchain technology? where altering one block breaks the chain—a built-in fraud detection system.
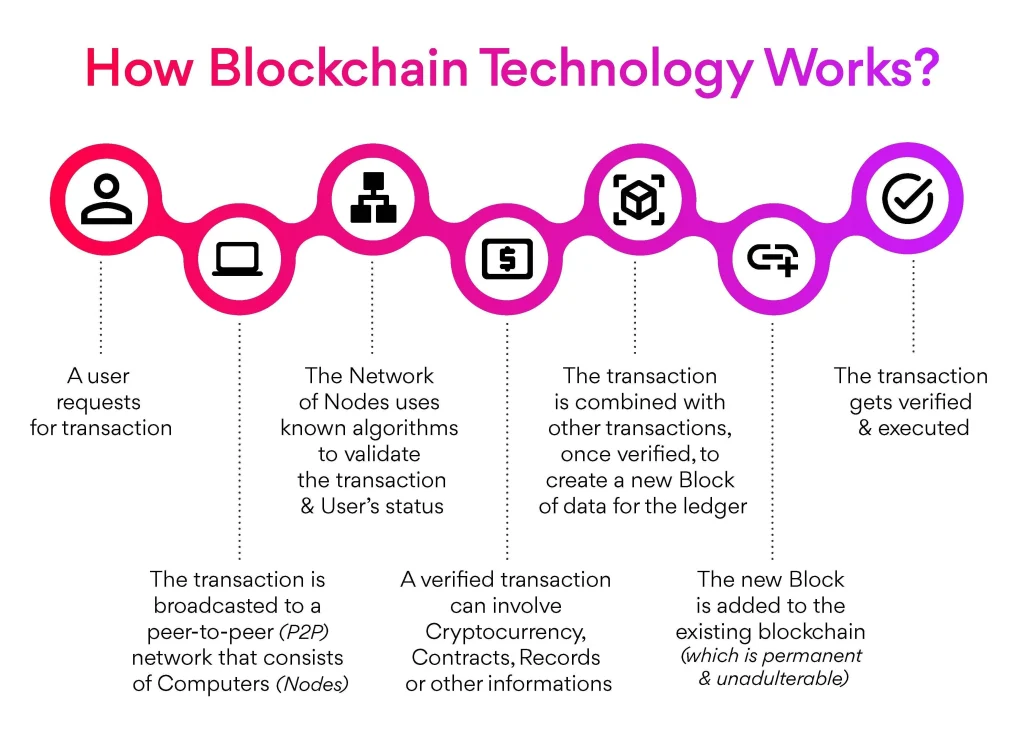
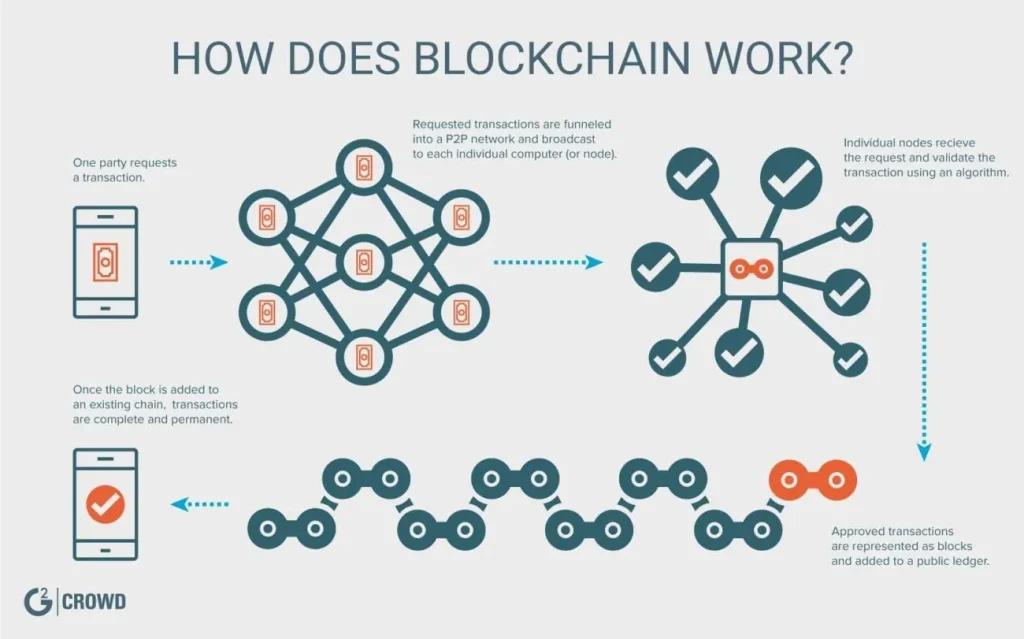
How Blockchain Works
Let’s break down how blockchain works in 5 stages:
- A Transaction Happens: Alice sends money to Bob.
- Broadcast to the Network: Thousands of nodes receive the data.
- Validation: Miners or validators confirm the transaction using consensus rules.
- Block Creation: The verified transaction is added to a block.
- Link to the Chain: The new block connects to the previous one, forming a permanent record.
No middleman, no delays, no corruption—just pure math and code enforcing trust.
Core Components of a Blockchain
1. Block
A digital container of data (e.g., money sent, file uploaded, vote cast).
2. Hash
A fingerprint of a block. If even 1 character changes, the hash breaks.
3. Node
Every computer on the network that stores a full copy of the blockchain.
4. Consensus Mechanism
How everyone agrees on the next valid block (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake).
5. Smart Contract
Code stored on blockchain that executes automatically (like Netflix autoplay).
Why Blockchain Is Revolutionary
Transparency
All participants see the same version of the truth.
Immutability
Once added, data cannot be changed—ideal for audit trails.
Decentralization
No single point of control—no central bank or authority needed.
Cost Efficiency
Reduces intermediaries like brokers, banks, or notaries.
Security
Hacking a blockchain means rewriting thousands of copies—nearly impossible.
Real-World Blockchain Use Cases (Beyond Crypto)
Finance
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) lets users borrow, lend, and trade without banks.
Supply Chain
Walmart uses blockchain to track food freshness. No more guessing who sent a spoiled mango.
Healthcare
Encrypted, shareable patient records across hospitals.
Voting
Blockchain ballots are traceable and tamper-proof—great for election security.
Digital Art
NFTs let artists sell verifiable digital ownership on the blockchain.
Fun fact: The Indian government is experimenting with blockchain in land registration and education certificates.
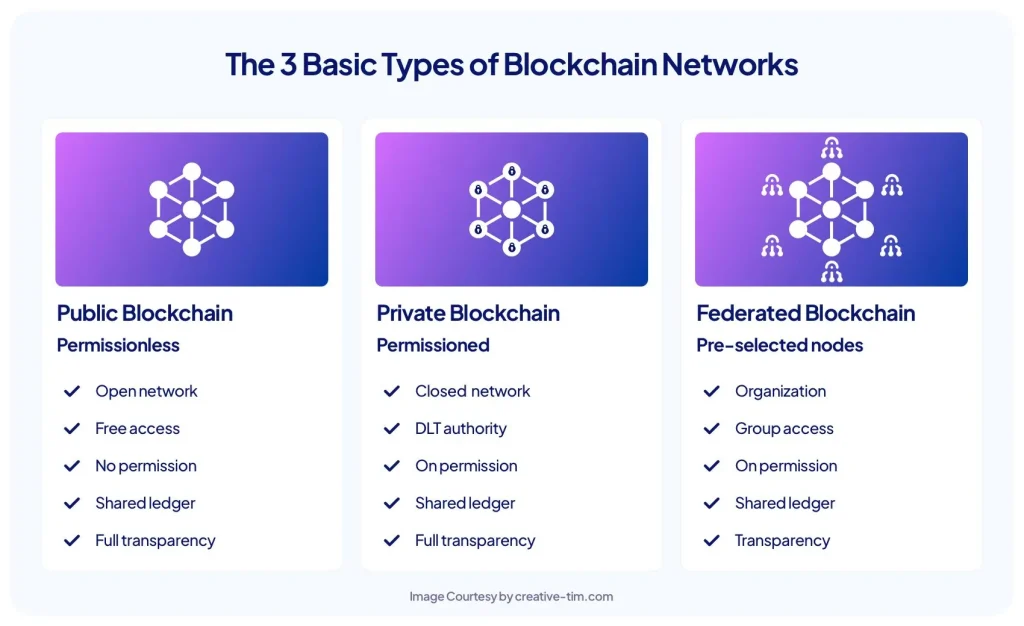
Public vs Private Blockchain
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Who can join? | Anyone | Invitation only |
| Speed & Cost | Slower, expensive | Faster, cheaper |
| Examples | Ethereum, Bitcoin | Hyperledger, Corda |
| Use Cases | Crypto, NFTs | Supply chain, Banking |
Public = Internet | Private = Intranet
That’s how you remember the difference.
Blockchain vs Traditional Databases
| Feature | Traditional Database | Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Mutability | Editable | Immutable |
| Cost | Cheaper | Sometimes costly |
| Trust | Manual | Built-in |
| Transparency | Private | Public (in many cases) |
Smart Contracts: Automation Without Humans
Smart contracts are code stored on blockchain that automatically executes when conditions are met.
Example:
“If you send ₹1,000 on July 1, I will ship your parcel.”
No delays, no cheating—it happens by code.
Used in:
- Insurance claims
- Supply chains
- Real estate
- Gaming (Web3)
Limitations of Blockchain
Even perfection has flaws:
Energy Consumption
Bitcoin mining uses more energy than some countries.
Fees
Gas fees on Ethereum can go as high as ₹5,000 per transaction during peak times.
Scalability
Some blockchains process only 7–30 transactions per second (vs Visa’s 24,000+ TPS).
Smart Contract Bugs
Code errors are irreversible. One line of wrong code can cause multi-crore losses.
How to Start: Blockchain for Beginners
You don’t need to be a developer to explore blockchain:
- Read Blogs: Try sites like CoinDesk, Cointelegraph, and Decrypt.
- Open a Wallet: MetaMask or Coinbase Wallet (free).
- Use a Test Network: Play with fake tokens, deploy a simple contract.
- Join a DAO: Participate in real blockchain governance.
- Take Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Khan Academy.
The Future of Blockchain
- Web3: Blockchain-powered internet where users own their data.
- Interoperability: Different chains connecting smoothly (e.g., Polkadot, Cosmos).
- AI + Blockchain: AI models using verifiable data for decisions.
- CBDCs: Central Bank Digital Currencies based on blockchain.
- Green Chains: Sustainable models like Solana and Algorand gaining traction.
The world’s biggest companies—Amazon, IBM, JPMorgan—are already integrating blockchain. The question is: are you?
Blockchain isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a shift in how we store, secure, and trust data.
And like Netflix revolutionized entertainment, blockchain is reshaping how we manage value, identity, and agreements.
With blockchain explained in simple terms, you’re now equipped to explore use cases, experiment with tools, and become part of this exciting transformation.
Whether you’re a student, marketer, techie, or entrepreneur—this blockchain for beginners guide is your launchpad.
FAQs
Q1: What is blockchain in one sentence?
A: Blockchain is a secure, decentralized ledger of data that can’t be changed once written.
Q2: Is blockchain only for Bitcoin?
A: No! It’s used in finance, supply chains, healthcare, and even education.
Q3: Can I learn blockchain without coding?
A: Yes. Many roles—analyst, strategist, marketer—don’t require coding.
Q4: Is blockchain safe?
A: Very. But smart contract bugs and scams can still be risky. Stay informed.
Q5: What’s the future of blockchain?
A: Web3, AI integrations, central bank digital currencies, and more real-world adoption.