Understanding Blockchain Technology: The Digital Revolution
What is Blockchain Technology and How Does It Work in 2025: Imagine a digital notebook that everyone can see but no one can cheat on.
That’s essentially what blockchain technology is – a revolutionary system that stores information across multiple computers in a way that makes it nearly impossible to hack, change, or manipulate.
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without changing all subsequent blocks.
Think of it as a chain of digital blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions, and these blocks are linked together chronologically to form an unbreakable chain.
Why Blockchain Matters in 2025
In today’s digital world, blockchain has evolved far beyond its initial association with cryptocurrencies.
The technology now powers everything from digital voting systems to supply chain tracking, making it one of the most transformative innovations of our time.
How Does Blockchain Work: A Simple Explanation

Step 1: Transaction Initiation
When someone wants to send digital money or information, they initiate a transaction. This could be anything from sending cryptocurrency to recording a medical record or tracking a product shipment.
Step 2: Digital Signature
The transaction is digitally signed using cryptography to prove it comes from the legitimate owner. This is like having an unforgeable digital signature that proves your identity.
Step 3: Network Broadcasting
The signed transaction is broadcast to the entire network of computers (called nodes) that maintain the blockchain. These computers are spread across the globe, making the system highly resilient.
Step 4: Validation Process
Network participants validate the transaction using predetermined rules. For example, they check if the sender has enough funds or if the transaction follows the network’s protocols.
Step 5: Block Creation
Valid transactions are bundled together into a block along with other transactions. Each block also contains a unique identifier called a hash and refers to the previous block’s hash, creating the “chain.”
Step 6: Consensus Achievement
The network must reach consensus that the new block is valid. Different blockchain networks use various consensus mechanisms, but the goal is the same: ensure everyone agrees on the transaction’s validity.
Step 7: Permanent Recording
Once consensus is reached, the new block is added to the blockchain and distributed across all network participants. The transaction is now complete and permanently recorded.
Latest Blockchain Advancements in 2025
AI-Powered Blockchain Analytics
Artificial Intelligence integration has revolutionized blockchain in 2025.
AI algorithms now analyze blockchain data to provide insights into market trends, detect fraudulent activities, and optimize network performance.
This combination enables predictive analytics and automated decision-making within blockchain systems.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Lightning Network and other Layer 2 solutions have matured significantly, enabling millions of transactions per second while maintaining security.
These solutions process transactions off the main blockchain and settle them in batches, dramatically reducing costs and increasing speed.
Quantum-Resistant Security
With quantum computing threats on the horizon, blockchain networks have implemented quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms in 2025.
These advanced security measures ensure blockchain systems remain secure even against future quantum computer attacks.
Carbon-Neutral Consensus
Proof of Stake mechanisms have become the dominant consensus model, reducing energy consumption by over 99% compared to older Proof of Work systems.
Major networks like Ethereum have successfully transitioned to these environmentally friendly alternatives.
Real-World Blockchain Applications in 2025
Digital Identity Management
Self-sovereign identity systems allow individuals to control their personal data without relying on centralized authorities.
Users can prove their identity for services like banking, healthcare, or travel without sharing unnecessary personal information.
Supply Chain Transparency
Companies like Walmart and Nestlé use blockchain to track food products from farm to store shelf.
Consumers can scan QR codes to see exactly where their food came from, when it was harvested, and how it was transported, ensuring authenticity and safety.
Digital Voting Systems
Several countries have implemented blockchain-based voting platforms that provide transparent, auditable elections while maintaining voter privacy.
These systems eliminate concerns about vote tampering and provide real-time, verifiable results.
Healthcare Records
Medical records stored on blockchain ensure patient data remains secure while allowing authorized healthcare providers to access complete medical histories instantly. This improves treatment quality and reduces medical errors.
Real Estate Tokenization
Property ownership can now be divided into digital tokens, allowing multiple investors to own fractions of expensive real estate. This democratizes real estate investment and increases market liquidity.
Industry Adoption Across Sectors
Banking and Finance
Traditional banks have embraced blockchain for cross-border payments, reducing transaction times from days to minutes while cutting costs by up to 80%.
JPMorgan’s JPM Coin and other bank-issued digital currencies facilitate instant settlements between institutions.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are being piloted or launched by over 100 countries in 2025, with China’s Digital Yuan and the European Union’s Digital Euro leading adoption.
Healthcare Industry
Beyond patient records, blockchain enables pharmaceutical supply chain verification, ensuring medications are authentic and haven’t been tampered with.
Clinical trial data stored on blockchain provides transparency and prevents data manipulation.
Gaming and Entertainment
Play-to-earn gaming models allow players to own in-game assets as NFTs that can be traded across different games and platforms. Virtual worlds use blockchain to establish true ownership of digital land and items.
Content creators use blockchain to prove ownership of digital art, music, and videos, enabling new monetization models and protecting intellectual property rights.
Government Services
Estonia’s e-Residency program uses blockchain to provide digital identity to global citizens, allowing them to access government services and start businesses entirely online. Other countries are following this model for various civic applications.
Energy Sector
Peer-to-peer energy trading platforms allow homeowners with solar panels to sell excess electricity directly to neighbors using blockchain smart contracts.
This creates more efficient energy markets and promotes renewable energy adoption.
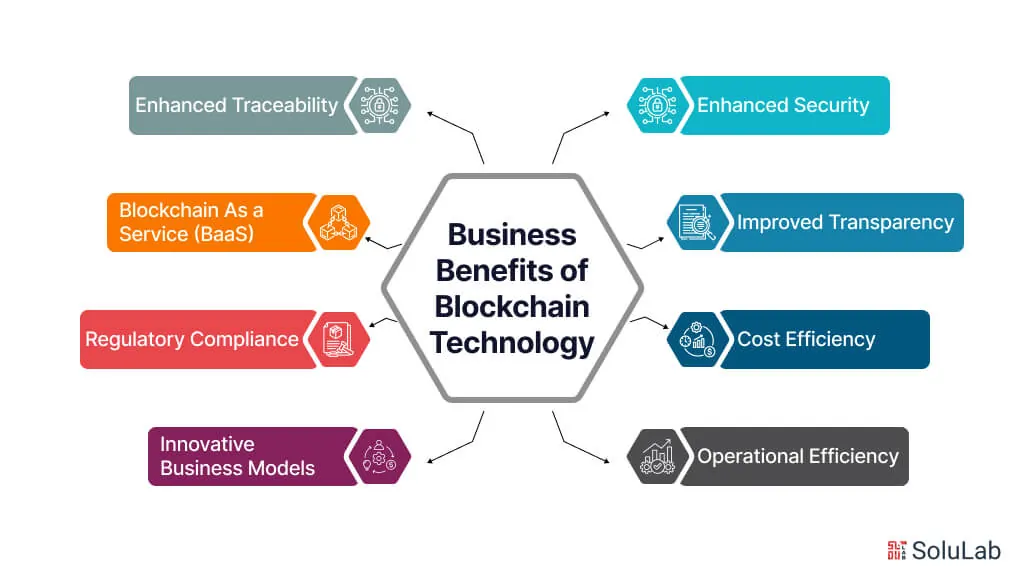
Key Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Enhanced Security
Cryptographic protection and distributed storage make blockchain systems extremely difficult to hack.
Even if some computers in the network are compromised, the system remains secure.
Reduced Costs
By eliminating intermediaries like banks or clearinghouses, blockchain reduces transaction fees and processing costs across many industries.
Increased Transparency
All network participants can view transaction history, promoting accountability and trust without compromising sensitive information.
Global Accessibility
Blockchain operates 24/7 without geographic restrictions, enabling global commerce and financial inclusion for underbanked populations.
Immutable Records
Once information is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted, providing a permanent and reliable record of events.
Challenges and Limitations
Scalability Concerns
While Layer 2 solutions help, some blockchain networks still face transaction throughput limitations compared to traditional systems like credit card networks.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Government regulations continue evolving, creating uncertainty for businesses and developers building blockchain applications.
Energy Consumption
Despite improvements, some blockchain networks still consume significant energy, particularly those using Proof of Work consensus mechanisms.
User Experience
Technical complexity can be intimidating for average users, though user-friendly interfaces are rapidly improving.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
Interoperability Advances
Cross-chain protocols are enabling different blockchain networks to communicate and share data, creating a more connected and efficient ecosystem.
Integration with IoT
Internet of Things devices are increasingly using blockchain for secure data sharing and automated payments, enabling smart cities and autonomous systems.
Mainstream Adoption
Traditional businesses are integrating blockchain into existing systems rather than building entirely new platforms, accelerating adoption across industries.
Enhanced Privacy Features
Zero-knowledge proofs and other privacy technologies allow blockchain systems to verify information without revealing sensitive details.
Getting Started with Blockchain
For beginners interested in blockchain technology:
- Start with educational resources to understand basic concepts
- Experiment with user-friendly wallets and small cryptocurrency transactions
- Explore blockchain explorers to see how transactions work in real-time
- Follow reputable news sources for latest developments
- Consider online courses from universities or blockchain organizations
Blockchain technology in 2025 represents a mature, transformative force reshaping how we store data, conduct transactions, and establish trust in digital interactions.
From its humble beginnings as the technology behind Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved into a comprehensive infrastructure supporting diverse applications across multiple industries.
The technology’s core benefits of security, transparency, and decentralization continue driving adoption, while recent advances in scalability, energy efficiency, and user experience address earlier limitations.
As blockchain integrates with AI, IoT, and other emerging technologies, its impact on society will only continue growing.
For individuals and businesses, understanding blockchain fundamentals is becoming increasingly important as digital transformation accelerates.
Whether through cryptocurrency adoption, supply chain transparency, or digital identity management, blockchain technology is creating new opportunities and efficiencies that will define the next decade of technological progress.
The future of blockchain looks bright, with continued innovation and mainstream adoption promising to deliver on the technology’s potential to create a more transparent, efficient, and equitable digital world.